Exploring The Gulf Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Guide
The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most significant natural and economic resources in the Americas. Spanning over 1.6 million square kilometers, it plays a crucial role in global trade, energy production, and biodiversity conservation. As one of the largest water bodies in the world, the Gulf of Mexico has become a focal point for environmental research, economic development, and tourism.
From its rich marine life to its extensive oil reserves, the Gulf of Mexico offers a wealth of opportunities and challenges. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of the Gulf of Mexico, covering its geography, ecology, economic importance, and the challenges it faces in the modern era.
Whether you're a researcher, traveler, or simply someone curious about the world's natural wonders, this guide will give you a comprehensive understanding of the Gulf of Mexico. Let's dive into the depths of this remarkable body of water and discover what makes it so unique.
Read also:Sophie Rain Onlyfans Leak Exploring The Facts Myths And Controversies
Table of Contents:
- Geography of the Gulf of Mexico
- Ecology and Marine Life
- Economic Importance
- Tourism Opportunities
- Environmental Challenges
- Historical Background
- Climate Change Impact
- Conservation Efforts
- Energy Resources
- Future Perspectives
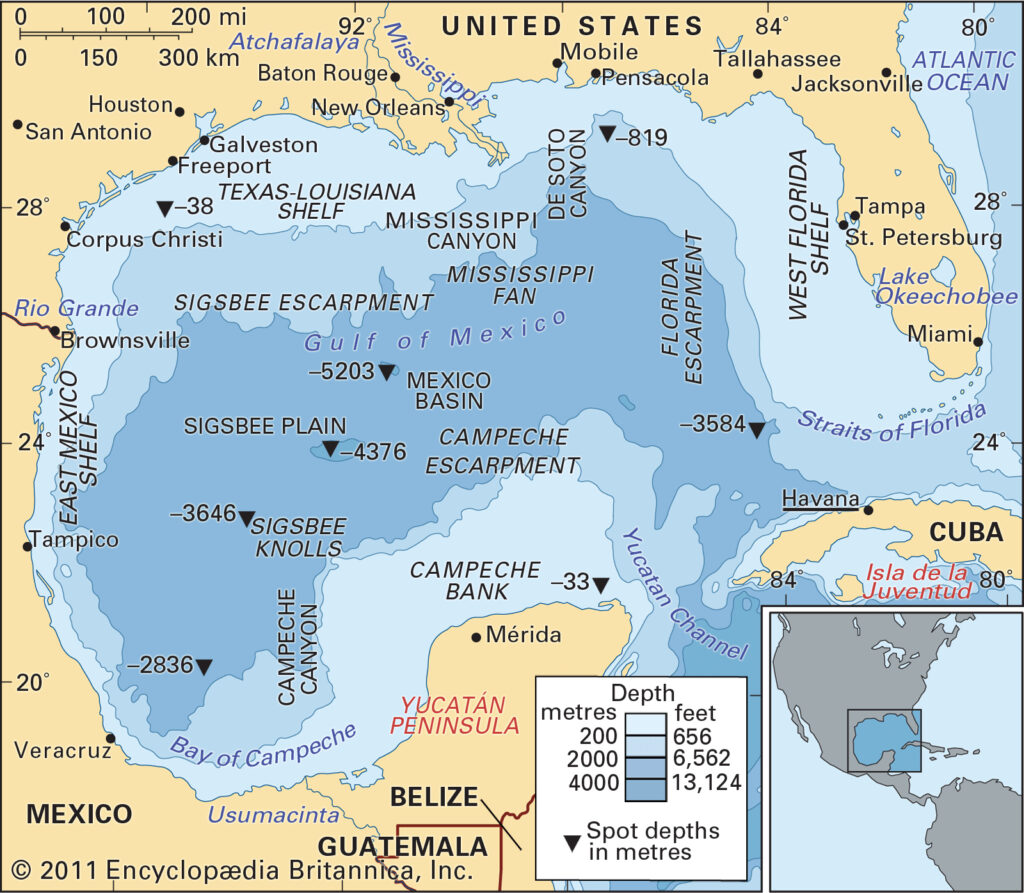
Geography of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a semi-enclosed sea bordered by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba. It is connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the Florida Straits and the Caribbean Sea via the Yucatán Channel. The Gulf's vast expanse covers an area of approximately 1.6 million square kilometers, making it one of the largest marginal seas in the world.
Key Features of the Gulf
Some of the most notable geographical features of the Gulf of Mexico include:
- The Florida Keys, a chain of islands at the southern tip of Florida.
- The Mississippi River Delta, which deposits vast amounts of sediment into the Gulf.
- The Sigsbee Deep, the deepest part of the Gulf, reaching depths of over 3,300 meters.
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the Gulf's coastline stretches over 5,000 kilometers, encompassing diverse ecosystems such as mangroves, estuaries, and coral reefs.
Ecology and Marine Life
The Gulf of Mexico is renowned for its rich biodiversity, supporting a wide range of marine species. From dolphins and sea turtles to countless fish species, the Gulf's ecosystem is both complex and fragile.
Key Marine Species
Some of the most prominent marine species found in the Gulf include:
Read also:Ariana Grande And Sabrina Carpenter Are They Friends Exploring Their Connection
- Bottlenose dolphins
- Kemp's ridley sea turtles
- Red snapper
- Blue crabs
Research conducted by the Environmental Defense Fund highlights the importance of preserving these species, as they play a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance of the Gulf.
Economic Importance of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a vital economic hub, contributing significantly to the economies of the United States, Mexico, and Cuba. Its resources and strategic location make it indispensable for various industries, including oil and gas, fishing, and shipping.
Oil and Gas Production
One of the most significant economic activities in the Gulf is the extraction of oil and gas. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the Gulf accounts for approximately 17% of total U.S. crude oil production. This industry provides thousands of jobs and generates billions of dollars in revenue annually.
Tourism Opportunities in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a popular destination for tourists from around the world. Its stunning beaches, vibrant culture, and rich history attract millions of visitors each year. Key attractions include:
- South Padre Island in Texas
- Mobile Bay in Alabama
- Cozumel in Mexico
These destinations offer a wide range of activities, from water sports and fishing to cultural festivals and historical tours.
Environmental Challenges Facing the Gulf
Despite its natural beauty and economic importance, the Gulf of Mexico faces numerous environmental challenges. Issues such as oil spills, overfishing, and habitat destruction threaten the long-term sustainability of this vital ecosystem.
Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
One of the most devastating environmental disasters in recent history occurred in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010. The Deepwater Horizon oil spill released millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf, causing widespread damage to marine life and coastal habitats. Efforts to mitigate the effects of this disaster are ongoing.
Historical Background of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico has a rich history, dating back thousands of years. Indigenous peoples such as the Maya and the Taino inhabited the region long before European explorers arrived. The arrival of Spanish explorers in the 16th century marked the beginning of a new era in the Gulf's history.
Key Historical Events
Some of the most significant historical events related to the Gulf of Mexico include:
- The Spanish exploration of the Gulf in the early 1500s.
- The establishment of New Orleans as a major port city in the 18th century.
- The development of offshore oil drilling in the 20th century.
Climate Change Impact on the Gulf of Mexico
Climate change poses a significant threat to the Gulf of Mexico. Rising sea levels, increased storm intensity, and ocean acidification are just a few of the challenges the region faces. Scientists warn that these changes could have profound effects on the Gulf's ecosystems and economies.
Adaptation Strategies
To address these challenges, governments and organizations are developing adaptation strategies. These include:
- Restoring coastal wetlands to protect against storm surges.
- Implementing sustainable fishing practices to preserve marine life.
- Investing in renewable energy sources to reduce carbon emissions.
Conservation Efforts in the Gulf of Mexico
Efforts to conserve the Gulf of Mexico's natural resources are ongoing. Organizations such as the Gulf of Mexico Alliance and the Nature Conservancy work tirelessly to protect the region's ecosystems and promote sustainable development.
Key Conservation Initiatives
Some of the most notable conservation initiatives include:
- The establishment of marine protected areas to safeguard critical habitats.
- The implementation of water quality improvement programs.
- The promotion of environmental education and community engagement.
Energy Resources in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a major source of energy resources, particularly oil and natural gas. Advances in technology have made it possible to extract these resources more efficiently and with less environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Potential
While fossil fuels remain a dominant force in the Gulf's energy sector, there is growing interest in renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. The Gulf's vast open waters and consistent wind patterns make it an ideal location for offshore wind farms.
Future Perspectives for the Gulf of Mexico
Looking ahead, the Gulf of Mexico will continue to play a vital role in global trade, energy production, and environmental conservation. However, addressing the challenges it faces will require collaboration and innovation from all stakeholders.
Call to Action
We invite you to join the conversation about the future of the Gulf of Mexico. Share your thoughts and ideas in the comments section below, and explore other articles on our site to learn more about this remarkable region. Together, we can ensure the Gulf remains a vibrant and sustainable resource for generations to come.
In conclusion, the Gulf of Mexico is a treasure trove of natural and economic resources. By understanding its geography, ecology, and economic importance, we can better appreciate its value and work towards its preservation. Let's continue to explore and protect this vital body of water, ensuring its legacy for future generations.
Article Recommendations