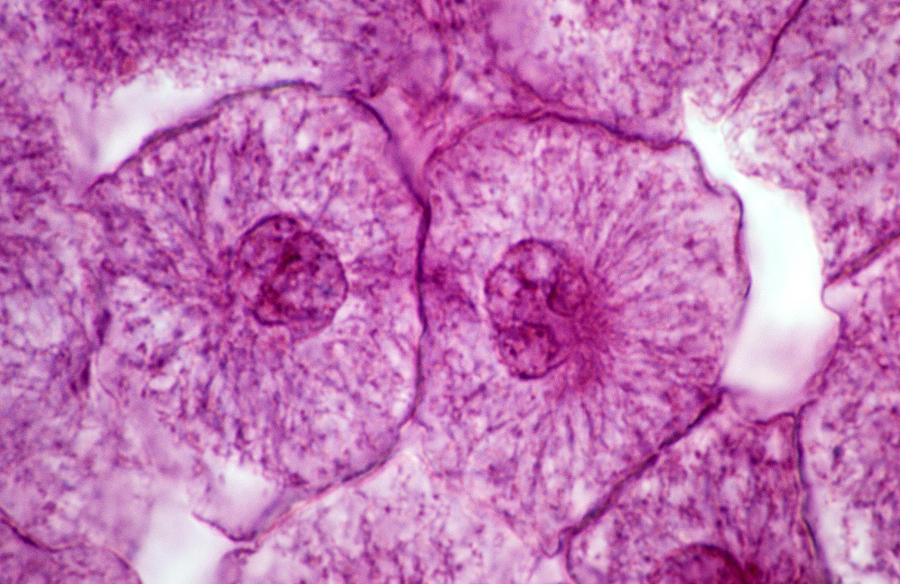
Unveiling The Mysteries Of Interphase In Real Cells: What You Need To Know
Interphase is often referred to as the "resting phase" of a cell's life cycle, but don't let that fool you. It's actually a super busy time where cells prepare for division and growth. Think of it like getting ready for a big event – you don’t just sit around, right? Interphase is the longest phase in the cell cycle, and it plays a crucial role in the overall health and functionality of cells. Without it, life as we know it wouldn’t function properly.
Now, let's dive into why interphase is so important. Cells are like little factories, and during interphase, they’re working overtime. They’re replicating DNA, producing proteins, and growing in size. All this prep work ensures that when the time comes for cell division, everything runs smoothly. Without interphase, cells would be a mess, and trust me, no one wants that.
So, what exactly happens during interphase? That’s what we’re here to explore. In this article, we’ll break down the different stages of interphase, discuss its importance, and even touch on some cool facts about how it impacts real cells in living organisms. Whether you’re a biology student or just someone curious about the inner workings of life, you’re in the right place. Let’s get started!
Read also:Junko Furuta Case The Dark Truth Behind Japans Most Infamous Crime
What Exactly is Interphase in Real Cells?
Interphase might sound simple, but it’s anything but. This phase is essentially the preparation period for cell division. It’s where cells get their act together before diving into the wild world of mitosis. During this time, cells focus on growth, DNA replication, and other essential processes that keep them functioning properly.
One of the coolest things about interphase is how it varies depending on the type of cell. For instance, some cells spend more time in interphase than others. This variation allows different cells to perform their specific roles in the body. Think of it like a well-organized team, where each member has a unique job to do.
The Importance of Interphase in Cell Functionality
Without interphase, cells wouldn’t be able to divide properly. It’s like trying to build a house without laying the foundation first. During this phase, cells ensure that all their components are in order, which is crucial for maintaining genetic stability. Any mistakes during interphase can lead to serious problems, such as mutations or even cancer.
Another key aspect of interphase is its role in growth. Cells need to grow in size and produce the necessary proteins to support their functions. This growth ensures that when the cell finally divides, both daughter cells are healthy and fully functional. It’s like making sure you have enough supplies before embarking on a long journey.
Breaking Down the Stages of Interphase
Interphase is divided into three main stages: G1, S, and G2. Each stage has its own unique set of tasks that contribute to the overall success of the cell cycle. Let’s take a closer look at what happens during each stage.
G1 Phase: The Growth Phase
G1 is all about growth. During this stage, cells increase in size and produce the proteins they’ll need for DNA replication. Think of it like a warm-up session before a big workout. Cells also check to make sure everything is in order before moving on to the next phase. If there are any issues, the cell can pause and fix them before continuing.
Read also:Zoe Perry Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
S Phase: The DNA Replication Phase
Now we’re getting into the nitty-gritty. The S phase is where DNA replication happens. This is a crucial step because it ensures that each daughter cell will have a complete set of chromosomes after division. The process involves unwinding the DNA strands and creating complementary strands, which is no small feat. It’s like copying a book word for word without making any mistakes.
G2 Phase: The Final Preparations
G2 is the last phase of interphase, and it’s all about final preparations. Cells continue to grow and produce proteins, but they also focus on checking the newly replicated DNA for errors. If any mistakes are found, they’re corrected before the cell moves on to mitosis. It’s like doing one last check of your luggage before heading to the airport.
How Interphase Impacts Real Cells in Living Organisms
Interphase isn’t just important for individual cells; it plays a vital role in the overall health of living organisms. For example, in humans, interphase ensures that cells divide properly, which is essential for growth and development. It also helps maintain tissue integrity and repair damaged cells.
In plants, interphase is crucial for growth and reproduction. Cells in the meristematic tissue spend a lot of time in interphase, allowing them to grow and divide as needed. This growth is what enables plants to reach their full potential and produce the fruits and vegetables we love.
The Role of Interphase in Cancer Development
While interphase is essential for healthy cell function, it can also play a role in cancer development. When cells spend too much time in interphase or fail to properly regulate their growth, it can lead to uncontrolled cell division. This uncontrolled growth is what causes tumors to form. Understanding interphase and how it works can help scientists develop better treatments for cancer.
Key Players in Interphase
Several key players are involved in the processes that occur during interphase. These include cyclins, CDKs (cyclin-dependent kinases), and other regulatory proteins. Cyclins are proteins that help regulate the cell cycle by activating CDKs, which in turn control the progression from one phase to the next.
Other important players include checkpoint proteins, which ensure that everything is in order before the cell moves on to the next phase. These checkpoints act like quality control officers, making sure that no mistakes are made during the process. If a checkpoint detects an issue, it can halt the cell cycle until the problem is resolved.
The Impact of Environmental Factors on Interphase
Environmental factors can also impact interphase and the overall health of cells. For example, exposure to radiation or certain chemicals can damage DNA, leading to errors during replication. This damage can result in mutations or even cancer if not properly repaired.
On the flip side, a healthy environment can support proper interphase function. Nutrients like vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in maintaining cell health, ensuring that they can perform their necessary functions during this phase. It’s like giving your cells the right fuel to keep them running smoothly.
Interphase in Different Types of Cells
Not all cells go through interphase in the same way. For example, nerve cells and muscle cells spend much of their lives in a state called G0, where they’re not actively preparing for division. This is because these cells don’t need to divide frequently; they focus more on maintaining their specialized functions.
On the other hand, cells in tissues like the skin and bone marrow spend a lot of time in interphase, as they need to divide frequently to replace old or damaged cells. This variation in interphase duration allows different types of cells to perform their specific roles in the body.
The Unique Challenges of Interphase in Specialized Cells
Specialized cells, like those in the nervous system, face unique challenges during interphase. Since they don’t divide often, they need to ensure that their DNA remains stable and error-free for long periods. This requires a different set of regulatory mechanisms than those used by rapidly dividing cells.
In addition, specialized cells often have additional checkpoints to ensure that any potential issues are caught early. This extra layer of protection helps maintain the overall health and functionality of these cells, which is crucial for the proper functioning of the organism.
Common Misconceptions About Interphase
There are a few common misconceptions about interphase that we should clear up. First, some people think that interphase is just a resting phase, but as we’ve seen, it’s anything but. It’s a highly active period where cells are preparing for division and growth.
Another misconception is that all cells spend the same amount of time in interphase. As we’ve discussed, this varies depending on the type of cell and its specific role in the body. Understanding these differences is key to appreciating the complexity of the cell cycle.
Why Interphase is Often Overlooked
Despite its importance, interphase is often overlooked in favor of more dramatic phases like mitosis. This is partly because it doesn’t involve the dramatic changes that occur during cell division. However, without interphase, mitosis wouldn’t be possible, so it’s just as important.
Future Research in Interphase
There’s still a lot we don’t know about interphase, and ongoing research is helping to shed light on this fascinating phase of the cell cycle. Scientists are exploring new ways to study interphase and its impact on cell function, which could lead to breakthroughs in medicine and biotechnology.
For example, understanding how interphase works in cancer cells could help develop new treatments that target specific stages of the cell cycle. Similarly, studying interphase in aging cells could provide insights into how to slow down the aging process and improve overall health.
Potential Applications in Medicine
Interphase research has the potential to revolutionize medicine. By understanding how cells prepare for division, scientists can develop new drugs and therapies that target specific stages of the cell cycle. This could lead to more effective treatments for a wide range of diseases, from cancer to genetic disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, interphase is a crucial phase in the cell cycle that plays a vital role in maintaining cell health and functionality. It’s where cells prepare for division, replicate DNA, and ensure that everything is in order before moving on to mitosis. Understanding interphase and how it works can help us better understand the complexities of life and develop new treatments for diseases.
So, the next time you hear someone refer to interphase as the "resting phase," you can set them straight. It’s anything but resting – it’s a busy, dynamic phase that’s essential for life. Now that you know more about interphase, why not share this article with your friends and help spread the word? And don’t forget to check out our other articles for more fascinating insights into the world of biology.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Interphase in Real Cells?
- The Importance of Interphase in Cell Functionality
- Breaking Down the Stages of Interphase
- How Interphase Impacts Real Cells in Living Organisms
- Key Players in Interphase
- The Impact of Environmental Factors on Interphase
- Interphase in Different Types of Cells
- Common Misconceptions About Interphase
- Future Research in Interphase
- Potential Applications in Medicine
Article Recommendations
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/interphase-58e3d4a45f9b58ef7e071ea0.jpg)